gonorrhoea
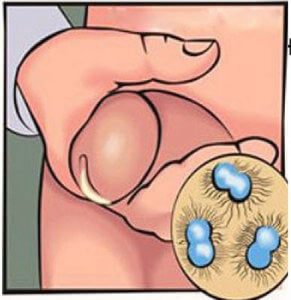
Gonorrhoea, mostly called the clap, is caused by bacteria. This nestles in the mucous skin on the inside of the vagina or the penis and multiplies itself there.
Symptoms of gonorrhoea
An infected area of the skin turns red, and there is usually some yellow and green discharge from the vagina or the penis. In anal or oral sex, the anus, and throat can become infected. Gonorrhoea is also transmitted during birth when the eyes of the baby come in contact with the wall of the vagina.
Symptoms of gonorrhoea are seen after a couple of days to a week after an infection. In boys, these symptoms are clearer than in girls, because the inside of the vagina is wider. Often in girls the symptoms of gonorrhoea are not noticed, because discharge from the vagina is a normal thing. She may feel abdominal pain, however. Boys usually do notice the discharge, which is mostly accompanied by pain during urinating.
Treatment of gonorrhoea
If you suspect that there is an infection due to recent unsafe sex, it is sensible to have yourself tested. This can be done by the family doctor, in special clinics, and in large hospitals. Testing gonorrhoea consists of making a smear of the surface of the mucous skin of the penis or vagina, or other infected area. The smear is then examined under the microscope. If the result is positive, you are given antibiotics. The person(s) with whom you have had sex should be informed so they too can have themselves tested. It is not wise to leave the infection in place, for then the bacteria can spread to the internal genitals. Thus, in the course of months or years, the testicles or the fallopian tubes can become painfully inflamed and then blocked.
